Part 2 Primer: Boostrap, CSS, Assets and More
Last Updated: January 2023
This tutorial extends the Earth Engine app developed in Part 1 and covers a wide range of additional topics for Tethys App development. In this tutorial you will learn how to add multiple pages to a Tethys App, create responsive layouts using the Boostrap CSS framework, upload files and manage them in the app, work with Google Earth Engine Assets, and add a REST API to your app.
This primer provides simple explanations for some of the concepts you and tools you will need to be familiar with for this tutorial. It also provides links to resources you can use to learn more about each topic. It is highly recommended that you take a little time to read through some of these valuable resources before continuing.
Bootstrap CSS Framework
Bootstrap is self-described as "the most popular HTML, CSS, and JavaScript framework". It provides HTML patterns, CSS, and a bit of JavaScript for building responsive websites. Tethys Platform includes Bootstrap as one of its built-in tools, so there is no need to download or install the libraries to use it in your app. At the time of writing, Tethys Platform provided Bootstrap version 5, which is not the latest release. Take care to use the correct version of the documentation whenever you search for Bootstrap help.
Responsive Web Design
Responsive web design is an approach to building websites that adjust to the device screen size and orientation. It employs a combination of flexible grids and layouts and an intelligent use of CSS.
Bootstrap Grid
Bootstrap provides a fluid grid system for creating just about any layout that you need. Using the grid system you can create a 2-column, 3-column, up to 12-column layout for larger screens. On narrow screens, no matter the layout, the columns stack on top of each other and fill the screen width. See Bootstrap Grid System for more details and tips.
Bootstrap Containers
The Bootstrap grid elements need to be placed inside one of the containers it provides. There are two types of containers to choose from: .container and .container-fluid. Using .container will create a responsive, fixed-width page with large margins, while the .container-fluid element will create a full-width page that changes dynamically if the viewport changes size. Both types of containers will be demonstrated in this tutorial. See Bootstrap Containers for more details.
Modals
Modals are a staple of web applications that can be used for dialogs and message boxes. Bootstrap provides a responsive modal with a JavaScript API to allow you bind to modal events and control it dynamically. See Bootstrap Modals for more details.
CSS Primer for Tethys Developers
CSS is a language that describes the style of an HTML document. While Bootstrap framework provides a good base for your app layouts, it is good to know some CSS to allow you to customize the look and feel of your app or make tweaks to the layout. A CSS document is composed of a list of rule-sets. Each rule-set is composed of a selector and a declaration block. The declaration block contains one or more rules that are composed of a property and a value. See w3schools CSS Tutorial or search "CSS" with your favorite search engine to find a wealth of examples and explanations of CSS.
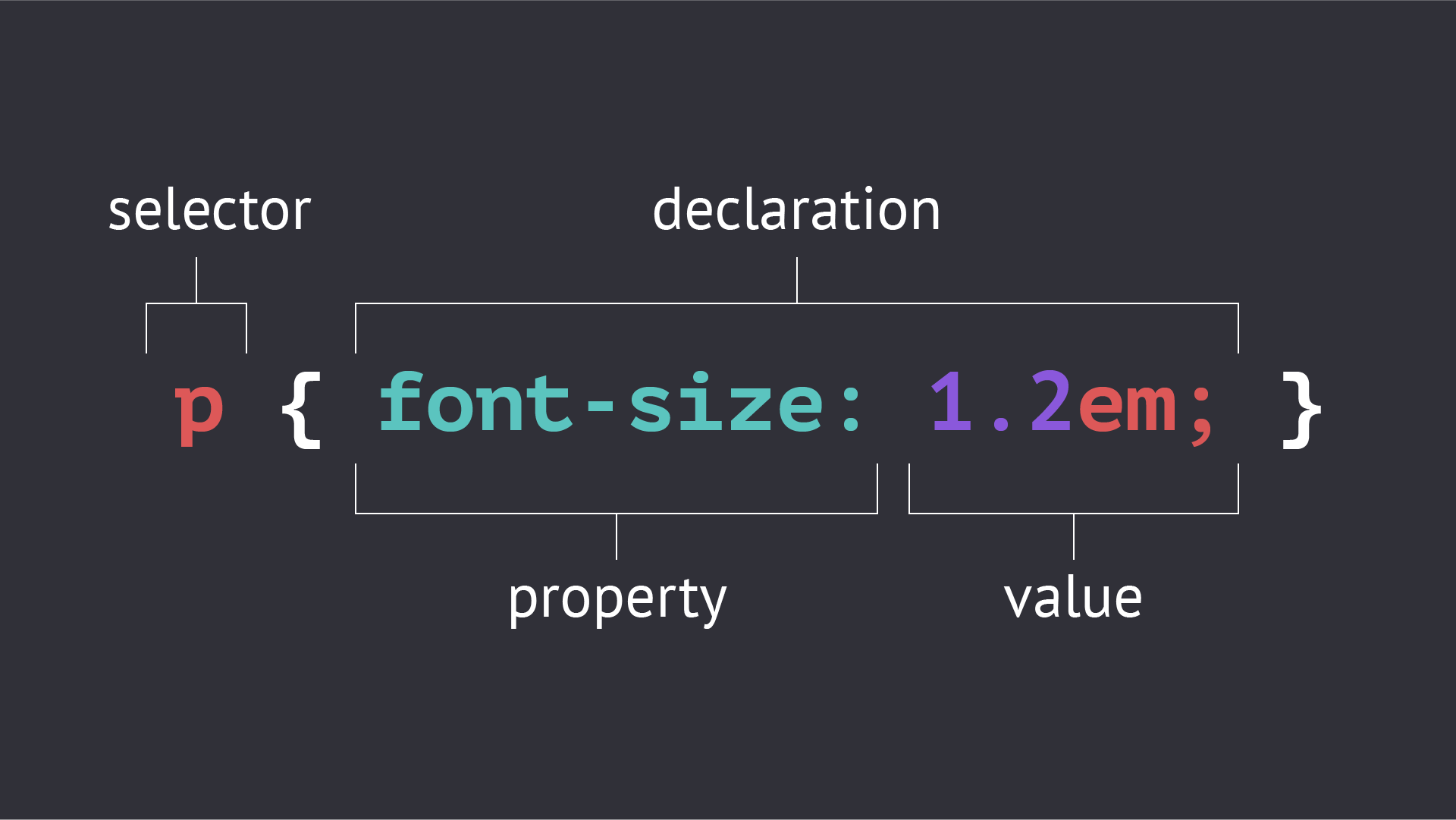
Selectors
The selector portion of a CSS rule-set defines which elements in the HTML document that the rules in the in the declaration block will be applied to. CSS provides syntax for selecting elements by id (#id), class (.class), and element type (div). Elements can also be selected based on their relationship to other elements or when they are in a certain state (e.g. hover). The selector statements can become quite complex. See w3schools CSS Selectors for more details.
Rules
The rules are compose of a property and value with each rule being separated by a semicolon. There are a lot of CSS properties for changing everything from the background color to the font of text in the element. Many of the values support a number of different units of length or formats. The best way to learn what the different properties do is to use them in a project. See w3schools CSS Reference for a fairly comprehensive list of CSS properties.
CSS Browser Tools
Many web browsers have built-in development tools including CSS inspectors. To save yourself from refreshing the page hundreds of times while developing CSS, we recommend you use the CSS tools in browser to tweak the styles and then copy the final rules into your CSS documents.
Google Earth Engine Assets
Datasets can be uploaded to your Google Earth Engine account to make them more readily available to your scripts that run on the server. Assets can be manually uploaded using the Asset Manager or programmatically as will be demonstrated in the File Upload tutorial. There are two types of assets: Table Assets and Raster Assets. Shapefiles and CSVs can be uploaded as Table Assets and GeoTIFFS and TFRecords can be uploaded as Raster Assets.
REST API Primer
REST is acronym for REpresentational State Transfer and is a software architectural style that defines a set of constraints for developing web services. Web resources are fairly abstract things referring to documents or some other representations of data. Each resource is uniquely identified by a URL called a URI (e.g. https://www.example.com/things/<id>/).
Different operations can be performed on a web resource by submitting a request to its URI with one of the HTTP verbs to indicate the operation to perform. The most commonly used HTTP verbs are GET and POST, but others include HEAD, DELETE, PUT, PATCH, CONNECT, OPTIONS, and TRACE. The POST verb is often used in place of the other verbs due to a lack of support of the other verbs historically. REST APIs should use appropriate response codes in their responses (e.g. 200 OK, 400 BAD REQUEST, 418 I'm a teapot).
The GET verb should only be used for operations that are non-destructive, such as data read operations. Any operation that changes, updates, or deletes data should be handled with POST (or the appropriate HTTP verb), because servers implement extra precautions with POST requests to make the requests more secure. For more information on RESTful APIs see: Wikipedia - Representational state transfer, REST API Tutorial, HTTP Status Codes.