Plot Data at a Location
Last Updated: January 2023
In the final tutorial you will add the ability for users to drop a point or draw a polygon and generate a time series of the selected dataset at that location. The following topics will be reviewed in this tutorial:
Tethys MapView Gizmo Drawing API
JQuery Load + Gizmo Strategy
GEE Geoprocessing
Adding New App Dependencies
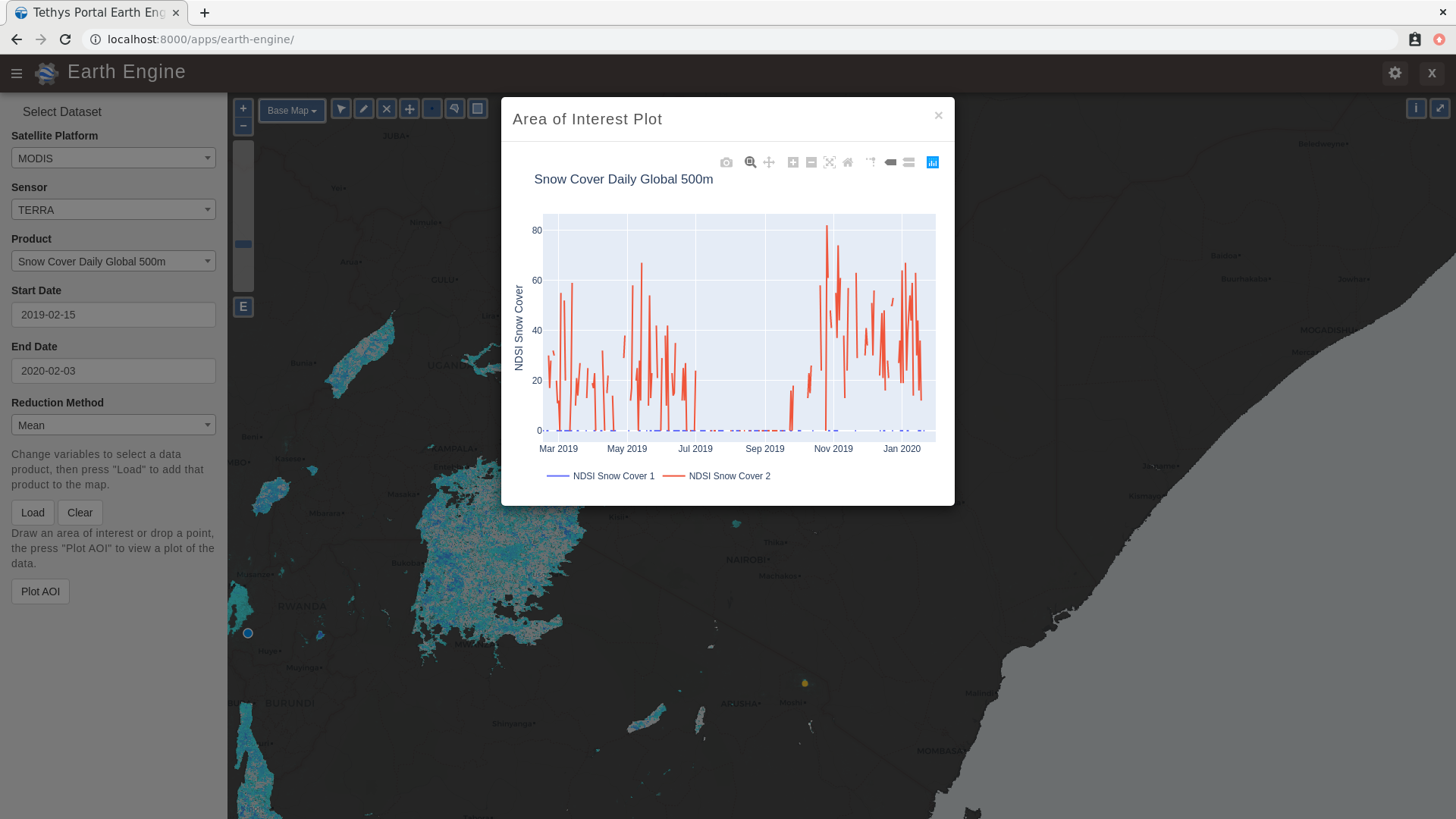
0. Start From Previous Solution (Optional)
If you wish to use the previous solution as a starting point:
git clone https://github.com/tethysplatform/tethysapp-earth_engine.git cd tethysapp-earth_engine git checkout -b vis-gee-layers-solution vis-gee-layers-solution-4.2
1. Create New GEE Function to Extract Time Series
In this step you'll expand the GEE functions to include a function that can extract time series at one or more points or polygons.
Install new dependency,
geojson, in Tethys environment:
conda install -c conda-forge geojson pandas
Add
geojsonas a dependency in theinstall.yml:
# This file should be committed to your app code.
version: 1.0
# This should be greater or equal to your tethys-platform in your environment
tethys_version: ">=4.0.0"
# This should match the app - package name in your setup.py
name: earth_engine
requirements:
# Putting in a skip true param will skip the entire section. Ignoring the option will assume it be set to False
skip: false
conda:
channels:
- conda-forge
packages:
- earthengine-api
- oauth2client
- geojson
- pandas
pip:
npm:
post:
Add
get_time_series_from_image_collectionfunction to thegee/methods.pymodule:
import geojson
import pandas as pd
def get_time_series_from_image_collection(platform, sensor, product, index_name, scale=30, geometry=None,
date_from=None, date_to=None, reducer='median'):
"""
Derive time series at given geometry.
"""
time_series = []
ee_product = EE_PRODUCTS[platform][sensor][product]
collection_name = ee_product['collection']
if not isinstance(geometry, geojson.GeometryCollection):
raise ValueError('Geometry must be a valid geojson.GeometryCollection')
for geom in geometry.geometries:
log.debug(f'Computing Time Series for Geometry of Type: {geom.type}')
try:
ee_geometry = None
if isinstance(geom, geojson.Polygon):
ee_geometry = ee.Geometry.Polygon(geom.coordinates)
elif isinstance(geom, geojson.Point):
ee_geometry = ee.Geometry.Point(geom.coordinates)
else:
raise ValueError('Only Points and Polygons are supported.')
if date_from is not None:
if index_name is not None:
indexCollection = ee.ImageCollection(collection_name) \
.filterDate(date_from, date_to) \
.select(index_name)
else:
indexCollection = ee.ImageCollection(collection_name) \
.filterDate(date_from, date_to)
else:
indexCollection = ee.ImageCollection(collection_name)
def get_index(image):
if reducer:
the_reducer = getattr(ee.Reducer, reducer)()
if index_name is not None:
index_value = image.reduceRegion(the_reducer, ee_geometry, scale).get(index_name)
else:
index_value = image.reduceRegion(the_reducer, ee_geometry, scale)
date = image.get('system:time_start')
index_image = ee.Image().set('indexValue', [ee.Number(date), index_value])
return index_image
index_collection = indexCollection.map(get_index)
index_collection_agg = index_collection.aggregate_array('indexValue')
values = index_collection_agg.getInfo()
log.debug('Values acquired.')
df = pd.DataFrame(values, columns=['Time', index_name.replace("_", " ")])
time_series.append(df)
except EEException:
log.exception('An error occurred while attempting to retrieve the time series.')
log.debug(f'Time Series: {time_series}')
return time_series
This function uses a Pandas DataFrame to store each time series. The DataFrame consists of two columns: Time and the name of the index. The column names will be used for the plot axes.
2. Create Endpoint for Extracting Time Series
The technique that will be demonstrated in this step will leverage the jQuery.load() method, which calls a URL and inserts the HTML returned into a target element. You'll create an endpoint that will call the get_time_series_from_image_collection function to get the times series and then render a plot using the Tethys PlotlyView gizmo. Then simply call the endpoint with jQuery.load() and target the content area of the plot modal to load the plot into the modal.
The
generate_figurehelper function creates a Plotly figure object from the given time series. Create a new module calledhelpers.pyin theearth_enginepackage with the following contents:
import pandas as pd
from plotly import graph_objs as go
def generate_figure(figure_title, time_series):
"""
Generate a figure from a list of time series Pandas DataFrames.
Args:
figure_title(str): Title of the figure.
time_series(list<pandas.DataFrame>): list of time series Pandas DataFrames.
"""
data = []
yaxis_title = 'No Data'
for index, df in enumerate(time_series):
column_name = df.columns[1]
yaxis_title = column_name
series_name = f'{column_name} {index + 1}' if len(time_series) > 1 else column_name
series_plot = go.Scatter(
x=pd.to_datetime(df.iloc[:, 0], unit='ms'),
y=df.iloc[:, 1],
name=series_name,
mode='lines'
)
data.append(series_plot)
figure = {
'data': data,
'layout': {
'title': {
'text': figure_title,
'pad': {
'b': 5,
},
},
'yaxis': {'title': yaxis_title},
'legend': {
'orientation': 'h'
},
'margin': {
'l': 40,
'r': 10,
't': 80,
'b': 10
}
}
}
return figure
The
get_time_series_plotfunction will call theget_time_series_from_image_collectionfunction with the parameters given and render aPlotlyViewgizmo from the results. Add a new controller calledget_time_series_plottocontrollers.py:
import geojson
from simplejson.errors import JSONDecodeError
from tethys_sdk.gizmos import PlotlyView
from .helpers import generate_figure
from .gee.methods import get_time_series_from_image_collection
@controller
def get_time_series_plot(request):
context = {'success': False}
if request.method != 'POST':
return HttpResponseNotAllowed(['POST'])
try:
log.debug(f'POST: {request.POST}')
platform = request.POST.get('platform', None)
sensor = request.POST.get('sensor', None)
product = request.POST.get('product', None)
start_date = request.POST.get('start_date', None)
end_date = request.POST.get('end_date', None)
reducer = request.POST.get('reducer', None)
index_name = request.POST.get('index_name', None)
scale = float(request.POST.get('scale', 250))
geometry_str = request.POST.get('geometry', None)
# Derived parameters
ee_product = EE_PRODUCTS[platform][sensor][product]
display_name = ee_product['display']
if not index_name:
index_name = ee_product['index']
try:
geometry = geojson.loads(geometry_str)
except JSONDecodeError:
raise ValueError('Please draw an area of interest.')
if index_name is None:
raise ValueError(f"We're sorry, but plotting {display_name} is not supported at this time. Please select "
f"a different product.")
time_series = get_time_series_from_image_collection(
platform=platform,
sensor=sensor,
product=product,
index_name=index_name,
scale=scale,
geometry=geometry,
date_from=start_date,
date_to=end_date,
reducer=reducer
)
log.debug(f'Time Series: {time_series}')
figure = generate_figure(
figure_title=display_name,
time_series=time_series
)
plot_view = PlotlyView(figure, height='200px', width='100%')
context.update({
'success': True,
'plot_view': plot_view
})
except ValueError as e:
context['error'] = str(e)
except Exception:
context['error'] = f'An unexpected error has occurred. Please try again.'
log.exception('An unexpected error occurred.')
return render(request, 'earth_engine/plot.html', context)
Create a new template called
templates/earth_engine/plot.htmlwith the following contents:
{% load tethys_gizmos %}
{% if plot_view %}
{% gizmo plot_view %}
{% endif %}
{% if error %}
<div class="alert alert-danger" role="alert">
<span>{{ error }}</span>
</div>
{% endif %}
Important
Notice that this template does not extend from any template like other Tethys templates. It should contain only the HTML that will be inserted into the modal.
Notice also that the template will render an error message instead of the plot if an error is provided in the context.
3. Create a Modal for the Plot
In this step you'll add a Plot button and the modal for the plot to the controller and template.
Add Plot AOI button to
homecontroller incontrollers.py:
plot_button = Button(
name='load_plot',
display_text='Plot AOI',
style='outline-secondary',
attributes={'id': 'load_plot'},
)
context = {
'platform_select': platform_select,
'sensor_select': sensor_select,
'product_select': product_select,
'start_date': start_date,
'end_date': end_date,
'reducer_select': reducer_select,
'load_button': load_button,
'clear_button': clear_button,
'plot_button': plot_button,
'ee_products': EE_PRODUCTS,
'map_view': map_view
}
Add Plot AOI button to the
app_navigation_itemsblock of thetemplates/earth_engine/home.htmltemplate:
{% block app_navigation_items %}
<li class="title">Select Dataset</li>
{% gizmo platform_select %}
{% gizmo sensor_select %}
{% gizmo product_select %}
{% gizmo start_date %}
{% gizmo end_date %}
{% gizmo reducer_select %}
<p class="help">Change variables to select a data product, then press "Load" to add that product to the map.</p>
{% gizmo load_button %}
{% gizmo clear_button %}
<p class="help mt-2">Draw an area of interest or drop a point, the press "Plot AOI" to view a plot of the data.</p>
{% gizmo plot_button %}
{% endblock %}
Add a new Bootstrap Modal for displaying the plot to the
after_app_contentblock of thetemplates/earth_engine/home.htmltemplate:
{% block after_app_content %}
<!-- Plot Modal -->
<div class="modal fade" id="plot-modal" tabindex="-1" role="dialog" aria-labelledby="plot-modal-label">
<div class="modal-dialog" role="document">
<div class="modal-content">
<div class="modal-header">
<h5 class="modal-title" id="plot-modal-label">Area of Interest Plot</h5>
<button type="button" class="btn-close" data-bs-dismiss="modal" aria-label="Close"></button>
</div>
<div class="modal-body">
<div id="plot-container"></div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<!-- End Plot Modal -->
<div id="ee-products" data-ee-products="{{ ee_products|jsonify }}"></div>
<div id="loader">
<img src="{% static 'earth_engine/images/map-loader.gif' %}">
</div>
{% endblock %}
Temporarily bind the
clickevent of the Plot AOI button to the show modal action (in thebind_controlsmethod ofpublic/js/gee_datasets.js):
$('#load_plot').on('click', function() {
$('#plot-modal').modal('show');
});
4. Stub Out the Plot JavaScript Methods
Add the following module function declarations to the PRIVATE FUNCTION DECLARATIONS section of
public/js/gee_datasets.js:
// Time Series Plot Methods
var get_geometry, update_plot, show_plot_modal;
Add the following module function stubs to the PRIVATE FUNCTION IMPLEMENTATIONS section of
public/js/gee_datasets.js, just below theclear_mapmethod:
// Time Series Plot Methods
get_geometry = function() {};
update_plot = function() {};
show_plot_modal = function() {};
Note
The lines that define empty functions (e.g.: update_plot = function() {};) are method stubs that will be implemented in future steps.
5. Add a Loading GIF for the Plot Modal
In this step you'll add a loading image to the modal whenever it is shown, replacing whatever contents was there previously. This will be replaced by the loaded plot once it is finished loading. Launching the modal again, will replace the previous plot with the loading image and so on.
Download this
animated plot loading imageor find one that you like and save it to thepublic/imagesdirectory.Create a new stylesheet called
plot.cssinpublic/csswith the following contents:
#plot-loader {
display: flex;
align-items: center;
width: 100%;
justify-content: center;
flex-direction: column;
}
#plot-loader p {
text-align: center;
}
#plot-modal .modal-body {
min-height: 480px;
}
.modal-dialog {
max-width: 70vw;
margin: 1.75rem auto;
}
Include the
plot.cssstylesheet in thehome.htmltemplate:
{% block content_dependent_styles %}
{{ block.super }}
<link rel="stylesheet" href="{% static 'earth_engine/css/map.css' %}" />
<link rel="stylesheet" href="{% static 'earth_engine/css/loader.css' %}" />
<link rel="stylesheet" href="{% static 'earth_engine/css/plot.css' %}" />
{% endblock %}
Tip
Click on the Plot AOI button to open the modal before and after adding the plot.css styles to see how the styles change the position of the loading GIF in the modal.
Replace the
show_plot_modalmethod stub inpublic/js/gee_datasets.jswith the following implementation:
show_plot_modal = function() {
$('#plot-container').html(
'<div id="plot-loader">' +
'<img src="/static/earth_engine/images/plot-loader.gif">' +
'<p>Loading... This may take up to 5 minutes. Please wait.</p>' +
'</div>'
);
$('#plot-modal').modal('show');
};
To allow us to verify that the loading GIF appears in the modal when we update it, add a
clickevent on theload_plotbutton to temporarily call the newshow_plot_modalmethod. Add the following to the bottom of thebind_controlsmethod ofpublic/js/gee_datasets.js:
$('#load_plot').on('click', function() {
show_plot_modal();
});
Verify that the loading GIF appears in the modal when it is opened. Browse to http://localhost:8000/apps/earth-engine in a web browser and login if necessary. Click on the Plot AOI button to open the modal. The modal should show the loading GIF and it should be centered in the modal.
6. Implement Plotting Capability
In this step you'll use the native drawing capabilities of the Tethys MapView to allow the user to draw points and polygons on the map. Then you'll retrieve the drawn geometry in our JavaScript and send it with the other control values to the jQuery.load() call to the get-time-series-plot endpoint.
Enable the drawing controls in the
MapViewdefinition in thehomecontroller incontrollers.py:
from tethys_sdk.gizmos import MVDraw
map_view = MapView(
height='100%',
width='100%',
controls=[
'ZoomSlider', 'Rotate', 'FullScreen',
{'ZoomToExtent': {
'projection': 'EPSG:4326',
'extent': [29.25, -4.75, 46.25, 5.2]
}}
],
basemap=[
'CartoDB',
{'CartoDB': {'style': 'dark'}},
'OpenStreetMap',
'Stamen',
'ESRI'
],
view=MVView(
projection='EPSG:4326',
center=[37.880859, 0.219726],
zoom=7,
maxZoom=18,
minZoom=2
),
draw=MVDraw(
controls=['Pan', 'Modify', 'Delete', 'Move', 'Point', 'Polygon', 'Box'],
initial='Pan',
output_format='GeoJSON'
)
)
Include the
PlotlyViewGizmo dependencies in thetemplates/earth_engine/home.htmltemplate:
{% block import_gizmos %}
{% import_gizmo_dependency plotly_view %}
{% endblock %}
Update the
clickevent on theload_plotbutton to call the newupdate_plotmethod (in thebind_controlsmethod):
$('#load_plot').on('click', function() {
update_plot();
});
Replace the
get_geometrymethod stub inpublic/js/gee_datasets.jswith the following implementation:
get_geometry = function() {
// Get drawn geometry from embedded textarea of Tethys Map View
let geometry_json = $('#map_view_geometry').val() || null;
return geometry_json;
};
Update the
collect_datamethod inpublic/js/gee_datasets.jsto callget_geometryand return its result with the other data it collects:
collect_data = function() {
let data = {
platform: m_platform,
sensor: m_sensor,
product: m_product,
start_date: m_start_date,
end_date: m_end_date,
reducer: m_reducer,
geometry: get_geometry()
};
return data;
};
Replace the
update_plotmethod inpublic/js/gee_datasets.jswith the following implementation:
update_plot = function() {
let data = collect_data();
show_plot_modal();
$('#plot-container').load('get-time-series-plot/', data);
};
7. Test and Verify
Browse to http://localhost:8000/apps/earth-engine in a web browser and login if necessary. Verify the following:
Load approximately one year of the the MODIS TERRA Land Servica Temperature and Emissivity dataset on the map.
Use the Point drawing tool to add a point to the map.
Press the Plot AOI button to initiate the time series query and plotting.
The plot should show a single time series of temperatures. The gaps in the time series indicate where data is missing, usually due to cloud cover.
Repeat the process using one of the polygon tools to verify that the data is being aggregated properly.
8. Solution
This concludes this portion of the GEE Tutorial. You can view the solution on GitHub at https://github.com/tethysplatform/tethysapp-earth_engine/tree/plot-data-solution-3.0 or clone it as follows:
git clone https://github.com/tethysplatform/tethysapp-earth_engine.git cd tethysapp-earth_engine git checkout -b plot-data-solution plot-data-solution-4.2