Orientation to Azure VM
Last Updated: November 2021
This tutorial provides an orientation to the Tethys Azure virtual machine (VM). It includes instructions for connecting to the VM, user accounts to use, descriptions of what is installed, and important directories and files.
Connect with SSH
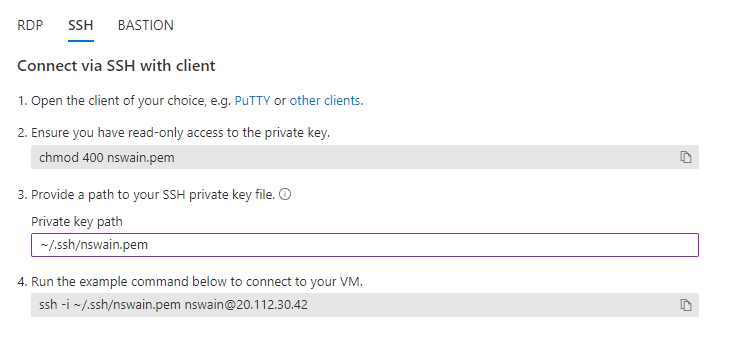
To connect to the Azure virtual machine via SSH, do the following:
Navigate to the overview page for the virtual machine resource.
If the virtual machine is not running, press the Start button.
Click on Connect from the tools at the top of the page and select SSH.
Follow the instructions to connect to the virtual machine via SSH.
Tethys User Account
The Tethys Portal image for Azure includes a tethys user account for maintenance of the Tethys installation. You should always be logged in to this account to run any tethys commands or install apps.
Change Tethys User Password
Before switching to the tethys user account, you should change the password using the following command:
sudo passwd tethys
Tip
Consider using a password generator to help you create strong passwords. For example, the xkpasswd generator is a tool based on an xkcd cartoon for creating secure passwords that are memorable.
Switch to Tethys User
To switch to the Tethys user from another account, use the su command (switch user):
su - tethys
Enter the password for the tethys user when prompted.
Important
Don't forget the dash (-)!
To exit the tethys user and return to your login user, run the exit command:
exit
Activate Conda Environment
Before running any tethys command in this or other tutorials, you'll need to activate the tethys Conda environment. After logging in as the tethys user, you'll notice that the base environment for Conda is automatically activated. Activate the tethys environment as normal:
conda activate tethys
Now you can run tethys commands:
tethys version
Tethys Home
Tethys Home is the directory where the portal_config.yaml is located. Use the TETHYS_HOME environment variable to locate the Tethys Home directory:
echo $TETHYS_HOME
You can also use TETHYS_HOME to change into the directory:
cd $TETHYS_HOME
Contents
List the contents of the TETHYS_HOME directory:
ls -l $TETHYS_HOME
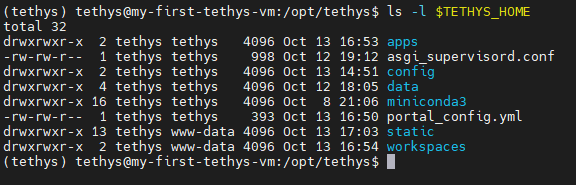
Figure 2. Contents of Tethys Home directory as given by ls command.
Here's a brief explanation of the important items in the Tethys Home directory:
apps: Directory for storing app source code.
config: Directory with configuration files used by the production installation.
data: Directory for storing data for GeoServer, THREDDS, etc.
miniconda3: Conda installation containing the
tethysConda environment.portal_config.yml: The primary configuration file for the Tethys Portal.
static: Location where static files are collected and served by NGINX.
workspaces: Location where workspaces for apps will be collected.
Database
Tethys Portal is configured to use a system-installed PostgreSQL database with the PostGIS extension installed.
psql
To connect to the database using psql, run the su command, but this time specifying the postgres user and a command to run with the -c option:
sudo su - postgres -c psql
Version
Using psql, run the following query to get the version of the PostgreSQL database:
SELECT version();
Run the following query in psql to get the version of PostGIS installed:
SELECT * FROM pg_available_extensions WHERE pg_available_extensions.name LIKE 'postgis';
Database Users
Run the following in psql to get a list of the database users:
\du
Important
The passwords of the database users should be changed from their default values. See Configure Azure VM tutorial for how to do this.
Databases
Run the following in psql to get a list of the databases:
\l
Quit psql
To quit psql run:
\q
Docker
Docker is installed on the image but not running by default. This is to make it easy for you to install the services your apps need such as a THREDDS or GeoServer. The Configure Azure VM tutorial describes the additional configuration that should be performed before using Docker.
Logs
In a production installation, you will need to examine logs to see errors when they occur. All logs for running processes on the server are located in the /var/log directory. Here's a list of the logs that are most helpful to use when debugging Tethys problems:
Daphne/Tethys Portal
The Daphne logs capture all of the logged information from Tethys Platform:
/var/log/tethys/access.log
/var/log/tethys/error.log
/var/log/tethys/out.log
NGINX
The NGINX logs are helpful to review when you get 502 errors or when you are debugging connection issues:
/var/log/nginx/access.log
/var/log/nginx/error.log
PostgreSQL
The PostgreSQL logs can be helpful when you encounter database errors, though these are rare for most Tethys applications:
/var/log/postgresql/postgresql-12-main.log
Start, Stop, Restart
The Daphne, NGINX, and PostgreSQL services are all managed using the systemctl command. You'll need to restart any of these services any time you make changes to the configuration. Use the following commands to start/stop/restart these services.
Daphne/Tethys
sudo systemctl status tethys.service
sudo systemctl start tethys.service
sudo systemctl stop tethys.service
sudo systemctl restart tethys.service
NGINX
sudo systemctl status nginx.service
sudo systemctl start nginx.service
sudo systemctl stop nginx.service
sudo systemctl restart nginx.service
PostgreSQL
sudo systemctl status postgresql@12-main.service
sudo systemctl start postgresql@12-main.service
sudo systemctl stop postgresql@12-main.service
sudo systemctl restart postgresql@12-main.service
Additional Resources
What's Next?
Now that you know how to connect to the VM and have a basic understanding of what is installed, you are ready to configure and customize the Tethys Portal. Don't skip out on this important next step!