Quotas Concepts
Last Updated: May 2022
This tutorial introduces Tethys Quotas API concepts for Tethys developers. The topics covered include:
Workspace Quotas
Creating custom quotas
Enforcing quotas
Managing quotas
Extended concepts from previous tutorials
0. Start From Advanced Solution (Optional)
If you wish to use the advanced solution as a starting point:
git clone https://github.com/tethysplatform/tethysapp-dam_inventory.git cd tethysapp-dam_inventory git checkout -b advanced-solution advanced-4.2
1. Workspace Quotas
In the Advanced Concepts tutorial we refactored the Model to use an SQL database, rather than files. However, we might want to store some data as files in case we want to export them later. This will also allow us to demonstrate the use of the built-in workspace qutoas that come with the Tethys Quotas API.
Add the @user_workspace argument to the
controllerdecorator and a user_workspace argument to theassign_hydrographcontroller. Write the hydrograph CSV with the dam id prepended to the filename to the user's workspace. The prepended id will be used later when handling a user deleting a dam they have created.import os ... @controller(url='hydrographs/assign', user_workspace=True) def assign_hydrograph(request, user_workspace): """ Controller for the Add Hydrograph page. """ # Get dams from database Session = app.get_persistent_store_database('primary_db', as_sessionmaker=True) session = Session() all_dams = session.query(Dam).all() # Defaults dam_select_options = [(dam.name, dam.id) for dam in all_dams] selected_dam = None hydrograph_file = None # Errors dam_select_errors = '' hydrograph_file_error = '' # Case where the form has been submitted if request.POST and 'add-button' in request.POST: # Get Values has_errors = False selected_dam = request.POST.get('dam-select', None) if not selected_dam: has_errors = True dam_select_errors = 'Dam is Required.' # Get File if request.FILES and 'hydrograph-file' in request.FILES: # Get a list of the files hydrograph_file = request.FILES.getlist('hydrograph-file') if not hydrograph_file and len(hydrograph_file) > 0: has_errors = True hydrograph_file_error = 'Hydrograph File is Required.' if not has_errors: # Process file here hydrograph_file = hydrograph_file[0] success = assign_hydrograph_to_dam(selected_dam, hydrograph_file) # Remove csv related to dam if exists for file in os.listdir(user_workspace.path): if file.startswith("{}_".format(selected_dam)): os.remove(os.path.join(user_workspace.path, file)) # Write csv to user_workspace to test workspace quota functionality full_filename = "{}_{}".format(selected_dam, hydrograph_file.name) with open(os.path.join(user_workspace.path, full_filename), 'wb+') as destination: for chunk in hydrograph_file.chunks(): destination.write(chunk) destination.close() # Provide feedback to user if success: messages.info(request, 'Successfully assigned hydrograph.') else: messages.info(request, 'Unable to assign hydrograph. Please try again.') return redirect(reverse('dam_inventory:home')) messages.error(request, "Please fix errors.") ...
Go to the Resource Quotas section of the admin pages and edit the
User Workspace Quotaas follows (must be done on administrator account):
Default -
2e-07(measured in GB so this converts to 214 bytes which allows for storing about 2 hydrographs to test the quota)Active -
EnabledImpose default -
Enabled
To test:
assign
hydrograph2.csvandhydrograph4.csv(from Sample Hydrographs) to two separate dams through the apptry to assign a third hydrograph (all of this must be done on a non-administrator account).
You should get an error page that advises you to visit the storage management pages and clean workspaces.
Do this now (see Manage User Storage for help) and try again to assign a hydrograph.
Because your user workspace is clear you should be able to assign another hydrograph.
Note
Quotas are not enforced on administrator users (i.e. staff/superusers). To manage quotas, login as administrator, but to test them, login as a normal user.
2. Clear Workspace Handler
Now that hydrograph files are stored to the user's workspace and the user can clear said workspace through their settings page, we will want to do some extra processing when they actually do clear their workspace. If the user deletes their hydrograph files we also want to remove the related hydrographs from the database.
First add
user_id = Column(Integer)as a column in the Dam model class. Also addcascade="all,delete"as an argument to thehydrographrelationship in theDammodel class and thepointsrelationship in theHydrographmodel class.class Dam(Base): """ SQLAlchemy Dam DB Model """ __tablename__ = 'dams' # Columns id = Column(Integer, primary_key=True) latitude = Column(Float) longitude = Column(Float) name = Column(String) owner = Column(String) river = Column(String) date_built = Column(String) user_id = Column(Integer) # Relationships hydrograph = relationship('Hydrograph', cascade="all,delete", back_populates='dam', uselist=False) class Hydrograph(Base): """ SQLAlchemy Hydrograph DB Model """ __tablename__ = 'hydrographs' # Columns id = Column(Integer, primary_key=True) dam_id = Column(ForeignKey('dams.id')) # Relationships dam = relationship('Dam', back_populates='hydrograph') points = relationship('HydrographPoint', cascade="all,delete", back_populates='hydrograph')
Note
Adding
cascade="all,delete"as an argument in an sqlalchemey model relationship causes the deletion of related records to be handled automatically. In this case, if hydrograph is removed from the database the hydrograph's points will also be deleted and if a dam is removed the connected hydrograph and its points will be removed.Then modify the
add_new_damfunction like so:def add_new_dam(location, name, owner, river, date_built, user_id): """ Persist new dam. """ # Convert GeoJSON to Python dictionary location_dict = json.loads(location) location_geometry = location_dict['geometries'][0] longitude = location_geometry['coordinates'][0] latitude = location_geometry['coordinates'][1] # Create new Dam record new_dam = Dam( latitude=latitude, longitude=longitude, name=name, owner=owner, river=river, date_built=date_built, user_id=user_id ) ...
Add
user_id=-1when initializingdam1anddam2in theinit_primary_dbfunction.def init_primary_db(engine, first_time): ... # Initialize database with two dams dam1 = Dam( latitude=40.406624, longitude=-111.529133, name="Deer Creek", owner="Reclamation", river="Provo River", date_built="April 12, 1993", user_id=-1 ) dam2 = Dam( latitude=40.598168, longitude=-111.424055, name="Jordanelle", owner="Reclamation", river="Provo River", date_built="1941", user_id=-1 ) ...
Then make the following changes to the
add_damcontroller:@controller(url='dams/add', permissions_required='add_dams') def add_dam(request): """ Controller for the Add Dam page. """ ... # Only add the dam if custom setting doesn't exist or we have not exceed max_dams if not max_dams or num_dams < max_dams: add_new_dam(location=location, name=name, owner=owner, river=river, date_built=date_built, user_id=request.user.id) else: ...
The changes that have been made to the model require us to drop the database tables for the Dam Inventory app and recreate them. Run the
tethys syncstorescommand with the--refreshoption to do this:tethys syncstores --refresh dam_inventory
Modify the
assign_hydrographcontroller again, this time to only allow users to assign hydrographs to dams that they have created.@controller(url='hydrographs/assign', user_workspace=True) def assign_hydrograph(request, user_workspace): """ Controller for the Add Hydrograph page. """ # Get dams from database Session = app.get_persistent_store_database('primary_db', as_sessionmaker=True) session = Session() all_dams = session.query(Dam).filter(Dam.user_id == request.user.id) ...
Finally, add the
pre_delete_user_workspacemethod to the app class inapp.py(see Tethys Quotas API for more details):class DamInventory(TethysAppBase): """ Tethys app class for Dam Inventory. """ ... @classmethod def pre_delete_user_workspace(cls, user): from .model import Dam Session = cls.get_persistent_store_database('primary_db', as_sessionmaker=True) session = Session() # Delete all hydrographs connected to dams created by user dams = session.query(Dam).filter(Dam.user_id == user.id) for dam in dams: if dam.hydrograph: session.delete(dam.hydrograph) session.commit() session.close()
Finally, remove the permissions restrictions on adding dams so that any user can add dams.
controllers.py:
@controller(url='dams/add') def add_dam(request): """ Controller for the Add Dam page. """ ...
base.html:
{% block app_navigation_items %} {% url 'dam_inventory:home' as home_url %} {% url 'dam_inventory:add_dam' as add_dam_url %} {% url 'dam_inventory:dams' as list_dam_url %} {% url 'dam_inventory:assign_hydrograph' as assign_hydrograph_url %} <li class="nav-item title">Navigation</li> <li class="nav-item"><a class="nav-link{% if request.path == home_url %} active{% endif %}" href="{{ home_url }}">Home</a></li> <li class="nav-item"><a class="nav-link{% if request.path == list_dam_url %} active{% endif %}" href="{{ list_dam_url }}">Dams</a></li> <li class="nav-item"><a class="nav-link{% if request.path == add_dam_url %} active{% endif %}" href="{{ add_dam_url }}">Add Dam</a></li> <li class="nav-item"><a class="nav-link{% if request.path == assign_hydrograph_url %} active{% endif %}" href="{{ assign_hydrograph_url }}">Assign Hydrograph</a></li> {% endblock %}
home.html:
{% block app_actions %} {% gizmo add_dam_button %} {% endblock %}
3. Custom Dam Quota
With the changes we made to the Dam model, we can now associate each dam with the user who created it and track how many dams each user created. In this part of the tutorial we will create a custom quota to restrict the number of dams a user can create. This will effectively replace the work we did in previous tutorials with the custom setting, max_dams. Instead of limiting the number of dams for the whole app through a custom setting we will restrict it per user with a custom quota.
Creating a custom quota is pretty simple. Create a new file called
dam_quota_handler.pyand add the following contents:from tethys_quotas.handlers.base import ResourceQuotaHandler from .model import Dam from .app import DamInventory as app class DamQuotaHandler(ResourceQuotaHandler): """ Defines quotas for dam storage for the persistent store. inherits from ResourceQuotaHandler """ codename = "dam_quota" name = "Dam Quota" description = "Set quota on dam db entry storage for persistent store." default = 3 # number of dams that can be created per user units = "dam" help = "You have exceeded your quota on dams. Please visit the dams page and remove unneeded dams." applies_to = ["django.contrib.auth.models.User"] def get_current_use(self): """ calculates/retrieves the current number of dams in the database Returns: Int: current number of dams in database """ # Query database for count of dams Session = app.get_persistent_store_database('primary_db', as_sessionmaker=True) session = Session() current_use = session.query(Dam).filter(Dam.user_id == self.entity.id).count() session.close() return current_use
Note
See ResourceQuotaHandler for an explanation of the different parameters.
Now go into the portal's
portal_config.ymlfile and add the dot-path of the handler class you just created in theRESOURCE_QUOTA_HANDLERSarray.settings: RESOURCE_QUOTA_HANDLERS: - tethysapp.dam_inventory.dam_quota_handler.DamQuotaHandler
Make sure the Tethys development server restarts by pressing
CTRL-Cand then runningtethys manage start.After re-starting tethys the
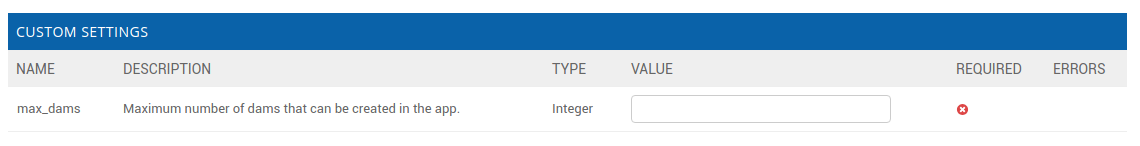
User Dam Quotashould be visible in theResource Quotasection of the admin pages. Click on it and make sure Active and Impose default are bothEnabled.Go into the app's settings page through the portal admin pages and delete the value for
max_damsin theCUSTOM SETTINGSsection. This will ensure that our custom quota is handling the amount of dams that can be added instead of the custom setting.To enforce the new dam quota set the
enforce_quotasargument on thecontrollersdecorator and add it to theadd_damcontroller.@controller(url='dams/add', enforce_quotas='user_dam_quota') def add_dam(request): """ Controller for the Add Dam page. """ ...
Note
We used the codename
user_dam_quotainstead of justdam_quotabecause Tethys Quotas appends what the quotaapplies_to(from the ResourceQuotaHandler class parameters) to the codename to differentiate between quotas on users or on apps.If we wanted to enforce our custom dam quota on an app as a whole we would need to add
"tethys_apps.models.TethysApp"to theapplies_toparameter in ourDamQuotaHandlerand then change the codename totethysapp_dam_quota.You can now test this by logging into a non-administrator account and trying to create more than 3 dams. You should be taken to another error page telling you that you have reached the limit on dams you can create.
4. Dam Quota Management
As is, the app would never allow a user to add a new dam once the quota was reached unless the portal administrator changed the dam quota default value (or made the quota inactive) or removed dams created by that user from the database. We will now add a way for a user to remove dams they have created through the list_dams controller.
Create the
delete_damfunction incontrollers.py:@controller(url='dams/{dam_id}/delete', user_workspace=True) def delete_dam(request, user_workspace, dam_id): """ Controller for the deleting a dam. """ Session = app.get_persistent_store_database('primary_db', as_sessionmaker=True) session = Session() # Delete hydrograph file related to dam if exists for file in os.listdir(user_workspace.path): if file.startswith("{}_".format(int(dam_id))): os.remove(os.path.join(user_workspace.path, file)) # Delete dam object dam = session.query(Dam).get(int(dam_id)) session.delete(dam) session.commit() session.close() messages.success(request, "{} Dam has been successfully deleted.".format(dam.name)) return redirect(reverse('dam_inventory:dams'))
Refactor the
list_damscontroller to add a Delete button for each dam. The code will restrict user's to deleting only dams that they created.@controller(name='dams', url='dams') def list_dams(request): """ Show all dams in a table view. """ dams = get_all_dams() table_rows = [] for dam in dams: hydrograph_id = get_hydrograph(dam.id) if hydrograph_id: url = reverse('dam_inventory:hydrograph', kwargs={'hydrograph_id': hydrograph_id}) dam_hydrograph = format_html('<a class="btn btn-primary" href="{}">Hydrograph Plot</a>'.format(url)) else: dam_hydrograph = format_html('<a class="btn btn-primary disabled" title="No hydrograph assigned" ' 'style="pointer-events: auto;">Hydrograph Plot</a>') if dam.user_id == request.user.id: url = reverse('dam_inventory:delete_dam', kwargs={'dam_id': dam.id}) dam_delete = format_html('<a class="btn btn-danger" href="{}">Delete Dam</a>'.format(url)) else: dam_delete = format_html('<a class="btn btn-danger disabled" title="You are not the creator of this dam" ' 'style="pointer-events: auto;">Delete Dam</a>') table_rows.append( ( dam.name, dam.owner, dam.river, dam.date_built, dam_hydrograph, dam_delete ) ) dams_table = DataTableView( column_names=('Name', 'Owner', 'River', 'Date Built', 'Hydrograph', 'Manage'), rows=table_rows, searching=False, orderClasses=False, lengthMenu=[[10, 25, 50, -1], [10, 25, 50, "All"]], ) context = { 'dams_table': dams_table, 'can_add_dams': has_permission(request, 'add_dams') } return render(request, 'dam_inventory/list_dams.html', context)
Test by deleting a dam or two (while logged in as the non-administrator) and trying to add new dams. This time you shouldn't be redirected to the error page, but should be able to add a dam like normal because you brought the number of dams created by the current user below the quota's default value.
5. Solution
This concludes the Quotas Tutorial. You can view the solution on GitHub at https://github.com/tethysplatform/tethysapp-dam_inventory or clone it as follows:
git clone https://github.com/tethysplatform/tethysapp-dam_inventory.git cd tethysapp-dam_inventory git checkout -b quotas-solution quotas-4.2