Layouts API
Last Updated: April 2022
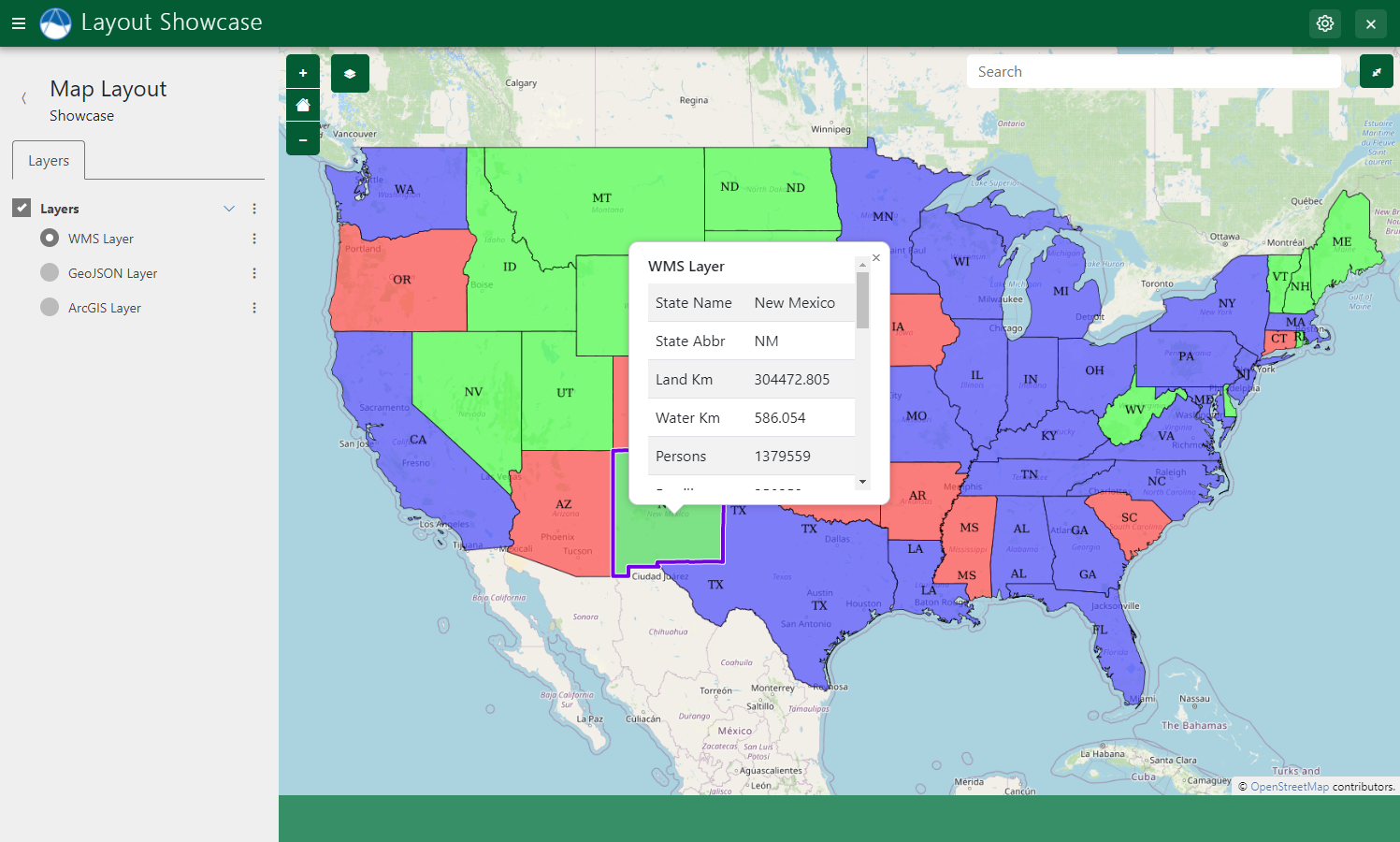
A Layout is a full featured and customizable view for Tethys Apps. They are different from Template Gizmos, which are only small piecies of that can be composed to create a full feature view, though many Layouts used Gizmos behind the scenes. For example, the Map Layout includes a fullscreen map-view with layer tree and includes advanced features feature selection, properties popups, and click and plot (Figure 1). In addition, Layouts provide rich JavaScript APIs that allow you to access the internal data and customize the dynamic behavoir of the view.
Supported Layouts
Here is a list of Layouts provided by Tethys Platform.
Layout Showcase App
The Layout Showcase App is a Tethys App can be installed in any Tethys Portal and includes live demonstrations and code samples of each Layout. See Layout Showcase App for instructions on installing the Layout Showcase App.
Tethys Layouts
Layouts are implemented using Django class-based views / contollers in a novel way that allows all the logic of complex views to be encapsulated in a single class. This makes them easy to implement, customize, and maintain. All Layouts inherit much of their core functionality from the TethysLayout class.
Class Based Views
TethysLayout is a Django class-based view, which is a controller implemented as a class instead of as a function. Class-based views have methods that coorespond with the different HTTP methods (e.g. get() -> GET and post() -> POST). For example, when a GET request is sent to a class-based view, it is routed to the get() method of the class. The get() method is structured in the same way as a function controller, accepting a request argument and returning a response.
as_controller()
Class-based views have an as_view() method that is used to return the entry point to the class (e.g.: entrypoint = TethysLayout.as_view()). The entrypoint is what is used to map the class-based view to a URL. Since Tethys uses the terminology "controller" instead of "view", TethysLayout classes have a as_controller() method that does the same thing as as_view().
Configure via Properties
Most of the configuration for a Layout is done by setting/overriding class properties in a subclass. This makes it easy to customize the behavoir of the Layout view. Here is an example of some of the configuration options for a Map Layout:
from tethys_sdk.layouts import MapLayout
class MyMapLayout(MapLayout):
map_title = 'My Map Layout'
map_subtitle = 'Subtitle'
basemaps = ['OpenStreetMap', 'ESRI', 'Stamen']
default_map_extent = [-65.69, 23.81, -129.17, 49.38] # CONUS bbox
max_zoom = 16
min_zoom = 2
Customize Behavoir via Methods
Some customization of Layouts is done by overriding methods of the class in a subclass. Many of the methods of a Layout exist expressly for this purpose. For example, to add layers to a Map Layout, the compose_map() method needs to be overridden in a subclass like so:
class MyMapLayout(MapLayout):
...
def compose_layers(self, request, map_view, *args, **kwargs):
"""
Add layers to the MapLayout and create associated layer group objects.
"""
# WMS Layer
usa_population = self.build_wms_layer(
endpoint='http://localhost:8181/geoserver/wms',
server_type='geoserver',
layer_name='topp:states',
layer_title='USA Population',
layer_variable='population',
visible=True, # Set to False if the layer should be hidden initially
)
# Add layer to map
map_view.layers.append(usa_population)
# Add layer to layer group
layer_groups = [
self.build_layer_group(
id='usa-layer-group',
display_name='United States',
layer_control='radio', # 'radio' or 'check'
layers=[
usa_population,
],
),
]
return layer_groups
Easy REST Endpoints
The TethysLayout provides a mechanism for easily setting up REST endpoints without the need to define additional URLs. This is one of the features that allows complex dynamic behavior of some Layouts to be contained in a single class. You can leverage this capability in your own Layout views to create custom REST endpoints.
First, create a new method on the subclass:
class MyMapLayout(MapLayout):
...
def update_data(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
"""
Custom REST method for updating data form Map Layout view.
"""
parms = request.POST
...
return JsonResponse({'success': True})
In the JavaScript for the view, use AJAX to call the URL of the view ('.') and add a method parameter with a value that is the name of the method on the class to call. The name can be specified using either underscores or hyphens (method=updated_data and method=updated-data are equivalent). For example:
fetch(".", {
method: 'POST',
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json',
},
body: JSON.stringify({
method: "update-data",
other: 1,
another: true
}),
}).then((response) => response.json()).then((data) => {
// Do something magical with your data :)
});
Custom Template and JavaScript
The HTML template for any Layout can be customized by creating an HTML document that extends the template of the Layout. This is most often done to add custom CSS or JavaScript to the template as shown in this example for a Map Layout:
{% extends "tethys_layouts/map_layout/map_layout.html" %}
{% load static %}
{% block scripts %}
{{ block.super }}
<script src="{% static 'layout_showcase/js/map.js' %}" type="text/javascript"></script>
{% endblock %}
Tell the Layout to use the custom template using the template_name property:
class MyMapLayout(MapLayout):
template_name = 'my_first_app/custom_map_layout.html'
...
API Documentation
- class tethys_layouts.views.tethys_layout.TethysLayout(**kwargs)
Base controller for all Tethys Layout views. Pass kwargs to as_controller() to override TethysLayout properties.
- get(request, *args, **kwargs)
Handle GET requests, either rendering the page or routing to class method.
- get_context(request, context, *args, **kwargs)
Hook to add additional content to context. Avoid removing or modifying items in context already to prevent unexpected behavior.
- Parameters:
request (HttpRequest) -- The request.
context (dict) -- The context dictionary.
- Returns:
modified context dictionary.
- Return type:
dict
- get_permissions(request, permissions, *args, **kwargs)
Hook to perform has_permission checks in. Values returned here are added to the context.
- Parameters:
request (HttpRequest) -- The request.
permissions (dict) -- The permissions dictionary with boolean values.
- Returns:
modified permisssions dictionary.
- Return type:
dict